Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
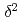 H and
H and 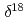 O of water in pores extracted by compression method; Effects of closed pores and comparison to direct vapor equilibration and laser spectrometry method
O of water in pores extracted by compression method; Effects of closed pores and comparison to direct vapor equilibration and laser spectrometry methodNakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*; Oyama, Takahiro*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Hydrology, 561, p.547 - 556, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.43(Engineering, Civil)no abstracts in English
Fukumoto, Masahiro; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 2001-002, 23 Pages, 2000/12
The soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt ( ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,
ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,  ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm
ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm , acetic acid : about 30mg/dm
, acetic acid : about 30mg/dm and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm
and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm ) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt (
) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt ( ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
Isogai, Takeshi*; Oda, Chie
JNC TN8400 2000-025, 48 Pages, 2000/09
Porewater chemistly in compacted bentonite would affect a performance of engineered barrier system in a high-level radioactive waste repository, whereas there are little information of the porewater based on experimental data. The previous study provided a new method of direct pH measurement for highly compacted bentonite system and demonstrated some tests for compacted bentonite samples (the dry densities: 1.6 [g/cm ] and 1.8 [g/cm
] and 1.8 [g/cm ]) both with the de-ionized water and with the NaCl solution. In this study, the solution equilibrated with low alkalinity cement were used in the direct pH measurement to see the effect of the composition of the external solutions, in which the bentonite column immersed. The result showed that the pH value of porewater in the cementitious condition was around 9 during the immersed time 1 to 3 months, while after 6 months became the porewater pH 10.6, which was equal to pH of the external solution.
]) both with the de-ionized water and with the NaCl solution. In this study, the solution equilibrated with low alkalinity cement were used in the direct pH measurement to see the effect of the composition of the external solutions, in which the bentonite column immersed. The result showed that the pH value of porewater in the cementitious condition was around 9 during the immersed time 1 to 3 months, while after 6 months became the porewater pH 10.6, which was equal to pH of the external solution.
Suzuki, Satoru; ; *
JNC TN8400 2000-020, 25 Pages, 2000/04
Nature of porewater in bentonite plays important roles on the mass transport in the compacted bentonite used as a physical and chemical buffer material of the multi-barrier system in the high level radioactive waste manegement Higher activation energies of diffusion in the compacted bentonite than those in the aqueous solution is due probably to change in molecular structure of water in the porewater. The Raman spectroscopy was applied to studying the structure of porewater in bentonite at room temperature. Bentonite (Kunipia F, 98-99wt% of Na-smectite) was mixed with ion-exchanged water by water content of 75, 80, 90, 95 and 98wt% of water or with 0.5M NaCl aqueous solution by 75 and 80wt% of NaCl solution. Intensity maxima of the spectra of ion exchanged water, NaCl solution and their porewater were observed near 3200 to 3250, 3400, 3630cm . These bands can be attributed to water molecules forming stronger hydrogen bond in this manner. Ratio of intensity, 3250cm
. These bands can be attributed to water molecules forming stronger hydrogen bond in this manner. Ratio of intensity, 3250cm /3400cm
/3400cm , increased from 0.97 to 1.1 with a decrease in water content of 100wt% (water) to 75wt%. On the other hand, intensity ratio of 3400cm
, increased from 0.97 to 1.1 with a decrease in water content of 100wt% (water) to 75wt%. On the other hand, intensity ratio of 3400cm /3250cm
/3250cm of NaCl aqueous solution, 80wt%and 75wt% were 0.92, 1.2 and 1.3, respectively. Since the Raman scattering near 3250cm
of NaCl aqueous solution, 80wt%and 75wt% were 0.92, 1.2 and 1.3, respectively. Since the Raman scattering near 3250cm was attributed to water molecule forming the strongest hydrogen bonding in the three bands, those changes in intensity ratio suggests an increase in number of water molecule forming strong hydrogen bond in porewater of the bentonite. The constrained porewater possibly results in the high activation energy of diffusion in the compacted bentonite.
was attributed to water molecule forming the strongest hydrogen bonding in the three bands, those changes in intensity ratio suggests an increase in number of water molecule forming strong hydrogen bond in porewater of the bentonite. The constrained porewater possibly results in the high activation energy of diffusion in the compacted bentonite.
Mori, Koji*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Nakagawa, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-064, 175 Pages, 2000/03
In this study, the following tasks have been performed in order to evaluate the stability of earthquake resistance for the engineered barrier system(EBS) of High Level Waste (HLW) geological isolation system. (1)validation studies for the liquefaction model. The function of single-phase analysis without interaction between soil and pore water in three-dimensional effective stress analysis code, which had been developed in this study, have been verified using by actual vibration test data. This fiscal year, some validation studies for the function of liquefaction analysis was conducted usig by actual measured data through the laboratory liquefaction test. (2)Supplemental Studies for JNC Second Progress Report. Through the JNC second progress report, it was considered that the stability of earthquake resistance of the engineered barrier system would be maintained under the major seismic event. At the same time we have recognized that several model parameters for joint-crack element, which takes into account for the response behavior of material discontinuous surface such as between overpack and buffer material, will become important in the response behavior of the whole EBS. This year, we have studied about several topics, which arise from technical discussion on JNC second progress report and we have discussed about total seismic stability of EBS. (3)Supplemental Studies for joint study with NRIDP. At this fiscal year, the joint study with National Research Institute for Disaster Prevention (NRIDP) will be final stage. UP to this day, incremental validation studies had been continued using by mesuared data obtained from vibration test. In this final stage, validation analysis has been conducted again using by current version new analysis code and maintained the validation data which will be contribute to the joint study mentioned above.
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Fujita, Hideki*; Kubo, Hiroshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-034, 212 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitlate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Kubo, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Hideki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-033, 95 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitrate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Tanai, Kenji; Sato, Haruo; *; *
JNC TN8400 99-045, 108 Pages, 1999/11
In the anaerobic environment in the deep underground water, carbon-steel overpack corrodes and generates molecular hydrogen. It is conceivable that this hydrogen either dissolves into the porewater of the buffer and migrates through the buffer. If the rate of aqueous diffusion of hydlogen is too low compared to the rate of hydrogen generation, the concentration of hydrogen at the overpack surface will increase until a solubility limit is attained and a free hydrogen gas phase forms. It is possible that the pressure in this accumulating gas phase will increase, affecting the stability of the buffer or the surrounding rock mass. There is also a concern of possible effects on nuclide migration, as it is also conceivable that the flow of gas could push out radionuclide-bearing porewater in the buffer when it floes through the buffer. As such, experimental and analytical study must be carried out on such phenomenon to evaluate such potential phenomena. (1)Diffusion experiment of dissolved hydrogen. According to the test result concerning the effective diffusion coefficient of the dissolved hydrogen in buffer material, the effective diffusion coefficient of reference buffer material (70wt% bentonite + 30wt% sand mixture, dry density 1.6Mg m ) ranges from 10
) ranges from 10 m
m s
s to 10
to 10 m
m s
s . The value of the effective diffusion coefficient measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg m
. The value of the effective diffusion coefficient measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg m is slightly smaller than the value in that for a dry density 1.6 Mg m
is slightly smaller than the value in that for a dry density 1.6 Mg m . And the effective diffusion coefficient at 60
. And the effective diffusion coefficient at 60 C tends to have slightly larger value than that at 25
C tends to have slightly larger value than that at 25 C. Test results from the foreign countries show the diffusion coefficient in the range between 10
C. Test results from the foreign countries show the diffusion coefficient in the range between 10 m
m s
s to 10
to 10 m
m s
s . Basically, these test results reported here are in the same range as these other results. (2)Gas permeability. Studies of the gas permeabinty of buffer material have been carried out by Pusch et al., Volckaert ...
. Basically, these test results reported here are in the same range as these other results. (2)Gas permeability. Studies of the gas permeabinty of buffer material have been carried out by Pusch et al., Volckaert ...
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-060, 12 Pages, 1999/10
Apparent diffusion coefficients(Da) of Cs(Cs ), Ni(Ni
), Ni(Ni ) and Se(SeO
) and Se(SeO
 ) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg
) in a Na-bentonite (Kunigel-V1) were measured for a dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O
with silica sand of 30 wt% at room temperature by in-diffusion method to evaluate the effect of the mixture of silica sand on Da in bentonite. The experiments for Cs and Ni were carried out under aerobic condition, but those for Se which is redox sensitive were carried out in an Ar glove-box (O concentration
concentration  0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
0.1 ppm). Consequently, no significant effect of silica sand mixture to the bentonite on Da values of Cs and Se was found, and the obtained Da values were approximately the same as those in the system without silica sand reported so far. On the other hand, Da values of Ni in bentonite with silica sand were 2 orders of magnitude lower than those in bentonite without silica sand obtained to date. The Da values of Ni reported so far were obtained using stable isotopic tracer and a tracer solution with fairly high Ni concentration compared with concentration used in this study was introduced. Additionally, it is known that distribution coefficient (Kd) of Ni on Na-montmorillonite which is the major constituent clay mineral of Kunigel-V1 decreases with increasing Ni concentration. Based on this, the abrupt decrease in Da values of Ni for bentonite with silica sand is considered to be due to the difference of sorption caused by the difference of Ni concentration in the porewater of bentonite.
Furuya, Kazuo*; *; Kodama, Toshio*
PNC TJ7705 97-001, 154 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English